Table of Contents
Toggle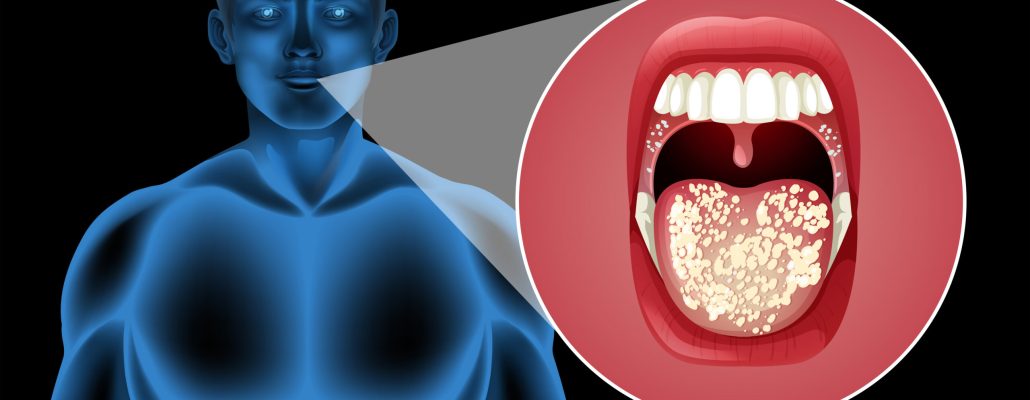
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, refers to a group of cancers that can occur in various parts of the mouth. Symptoms of oral cancer can resemble common issues such as sores or white patches in the mouth that may bleed.
It is also known as mouth cancer or oral cavity cancer, can develop due to a variety of factors. Here are some of the most common causes of mouth cancer:
- Tobacco use
- Alcohol consumption
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
- Sun exposure
- Poor oral hygiene
- Family history
- Age
- Gender
What Are the Symptoms of Oral Cancer?
The symptoms of oral cancer may vary depending on the location and stage of the cancer. The most common symptoms of mouth cancer include:
- Mouth sores or ulcers that don’t heal within a few weeks
- Red or white patches in the mouth or on the tongue
- Pain or difficulty swallowing
- A persistent sore throat or feeling that something is caught in the throat
- Hoarseness or a change in voice
- Numbness or tingling in the mouth or on the lips
- Swelling or lumps in the mouth, neck, or throat
- Loose teeth or dentures that no longer fit properly
- Earache or pain around the ear
- Unexplained weight loss
The symptoms of oral cancer may vary depending on the location and stage of the cancer. The most common symptoms of mouth cancer include:
If you notice any of these changes, contact your dentist or health care professional immediately.
This is a serious condition that can affect various parts of
- Lips
- Gums
- Tongue
- Inner lining of the cheeks
- Roof of the mouth
- Floor of the mouth (under the tongue)
Risks Factors Associated with Oral Cancer
There are several risk factors associated include:
- tobacco and alcohol use,
- human papillomavirus (HPV) infection,
- and a weakened immune system.
Prevention of Mouth Cancer
Here are some methods for lowering your risk of developing and preventing it:
- Avoid tobacco and alcohol: Tobacco and alcohol use are two of the most significant risk factors for mouth cancer. If you smoke or chew tobacco, consider quitting. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove food particles and bacteria that can cause mouth cancer.
- Get regular dental checkups: Visit your dentist at least twice a year for regular checkups. Your dentist can screen you for oral cancer and detect any signs early.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eat a diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables, which are high in antioxidants that can help prevent mouth cancer.
- Protect your lips from the sun: Use a lip balm that contains SPF to protect your lips from the harmful UV rays of the sun.
- Get vaccinated for HPV: The HPV vaccine can protect against certain strains of HPV that can cause oral cancer.
- Be aware of the signs and symptoms: If you notice any unusual lumps, bumps, or sores in your mouth or throat, or experience any pain or difficulty swallowing, see your doctor or dentist right away.
- By following these preventative measures, you can reduce your risk of developing mouth cancer and increase your chances of catching it early, when it is most treatable.
FAQ
• A sore, irritation, lump or thick patch in your mouth, lip, or throat.
• A white or red patch in your mouth.
• A sore throat or a feeling that something is caught in your throat.
• Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking.
• Difficulty moving your jaw or tongue.
Risk factors for developing mouth cancer include: smoking or using products that contain tobacco. drinking alcohol – smokers who are also heavy drinkers have a much higher risk compared to the population at large. infection with the human papilloma virus (HPV), the virus that causes genital warts.
Stage 0 cancer or carcinoma in situ (CIS) means your cancer is at a very early stage. Some doctors prefer to call this pre cancer. There are cancer cells but they are all contained within the lining of the mouth.
Stages I and II oral cavity cancer Most patients with stage I or II oral cavity cancers do well when treated with surgery and/or radiation therapy.
The most common symptom of oral cancer is an ulcer or sore in the mouth or on the lip that doesn’t heal. Another common symptom of oral cancer is pain in the mouth that doesn’t go away.

Designation: Consultant & Unit Chief/Program Director Head & Neck Oncology
Qualification: MBBS, MS(ORL-HNS), Fellowship Head & Neck Oncology
Department: Head and Neck Oncology Unit
Special interest: Reconstructive surgery and Minimal Invasive surgery in Head & Neck

4 thoughts on “What is Oral Cancer ?”