Table of Contents
Toggle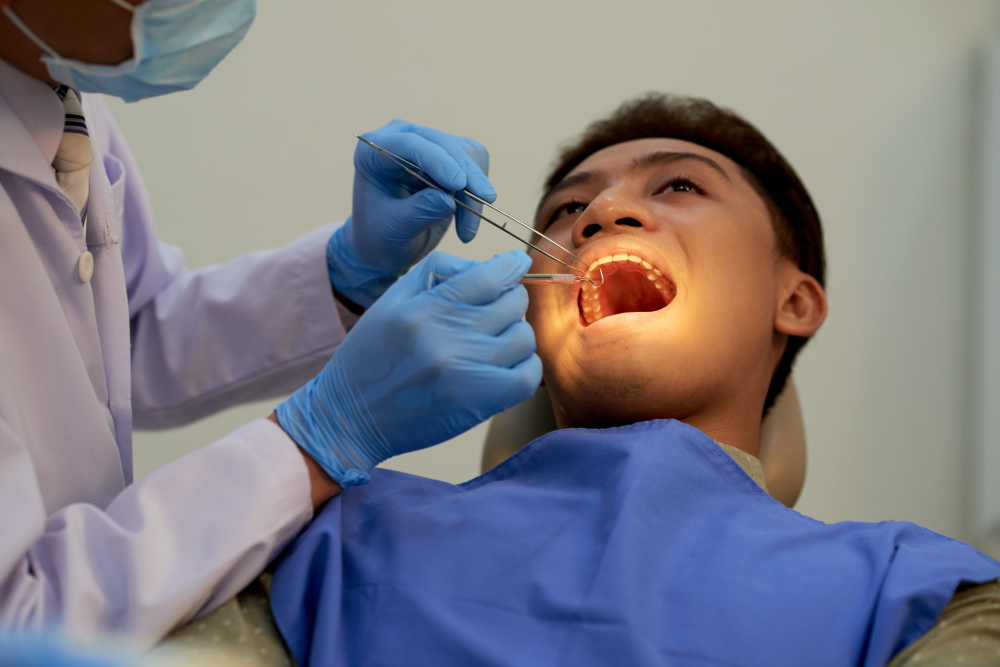
What is mouth cancer?
Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, is a type of cancer that affects the tissues of the mouth and throat. It can develop in any part of the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, gums, and cheeks, as well as the oropharynx (the back of the throat, including the tonsils) and the larynx (the voice box). In Nepal, Oral cancer cases were reported at 4.9 new cases per 100,000 men, based on a report generated. Mouth cancer is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if not caught and treated early. In this blog post, we will discuss everything you should know about Oral cancer, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Which Body Parts Are Affected From Mouth cancer?
The oral cavity is the area of the body that includes the lips, tongue, gums, cheeks, and hard and soft palates. It also includes the teeth, the floor of the mouth, and the area behind the wisdom teeth. Any of these areas can be affected by Oral cancer.
• The lips are the most common area for lip cancer to develop. Lip cancer typically appears as a sore or a scaly patch on the lip that does not heal.
• The tongue is another common area for Mouth cancer to develop. The cancerous cells may appear as a red or white patch on the tongue or as a sore that does not heal.
• The gums are also a common area for Oral cancer to develop. The cancerous cells may appear as a red or white patch on the gums or as a sore that does not heal.
• The cheeks, floor of the mouth, and the area behind the wisdom teeth are also areas that can be affected by Mouth cancer. In these areas, cancerous cells may appear as red or white patches or as sores that do not heal. It’s important to note that Oral cancer can also spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes in the neck.
Causes and Risk Factors of Mouth cancer
The exact cause of Mouth cancer is not known, but certain risk factors have been identified that increase the likelihood of developing the disease. The most common risk factors for Mouth cancer include the following:
• Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes or using smokeless tobacco (such as chewing tobacco or snuff) is the leading cause of Oral cancer.
• Alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol use is also a major risk factor for Oral cancer.
• Age: Mouth cancer is more common in people over the age of 50.
• HPV infection: Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a sexually transmitted virus that has been linked to certain types of Oral cancer, particularly in the oropharynx.
• Sun exposure: Long-term sun exposure increases the risk of lip cancer.
Symptoms of Mouth cancer
There can be a variety of symptoms associated with Mouth cancer, depending on the location and stage of the disease. Some of the most common symptoms are:
• You may experience pain or numbness at the corners of your mouth or on your lips
• Unhealed sores or lumps on the lips or in the mouth
• Having difficulty swallowing or speaking
• A change in the way the teeth fit together during the mouth is close.
• A white or red patch on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth
• A sore throat or hoarseness that does not go away
• A lump in the neck
• Weight loss.
It’ is important to know that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, such as cold sores or infections. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, be sure to see a doctor (oral/mouth cancer surgeon) or dentist to be examined.
Diagnosis of Mouth cancer
Diagnosing Mouth cancer involves identifying the signs and symptoms of the disease, as well as performing specific tests to confirm the diagnosis. If your doctor (Head and neck cancer surgeon) or dentist suspects that you may have Oral cancer, they will perform a thorough examination of your mouth and throat. They may also order additional tests, such as a biopsy, to confirm the diagnosis. Follow these steps to diagnosing Mouth cancer:
Oral examination:
The first step in diagnosing Oral cancer is a thorough examination of the mouth and throat. During this exam, the dentist or doctor (oral/ mouth cancer surgeon) will look for any suspicious sores, lumps, or discolorations in the oral cavity. They may also feel for any lumps or hard areas in the lymph nodes in the neck.
Biopsy:
If the oral examination reveals any suspicious areas, the next step is a biopsy. A biopsy involves removing a small piece of tissue from the suspicious area and analyzing it under a microscope. The only way to confirm an Oral cancer diagnosis is through a biopsy.
Imaging tests:
Imaging tests, such as an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI, may be used to determine the stage of cancer and to check if it has spread to other parts of the body.
Endoscopy:
An endoscopy may be performed to examine the throat, larynx, and pharynx. This procedure involves using a thin, lighted tube to look inside the throat.
Other tests:
Other tests such as blood tests, may be performed to check for the presence of cancer cells in the blood or to check the overall health of the patient.
Preventive Measures of Mouth cancer?
Preventing Mouth cancer is crucial to avoid the disease and its complications. Here are some preventive measures that can help reduce the risk of oral cancer:
Quit smoking:
Smoking and using smokeless tobacco are the leading cause of Oral cancer. Quitting smoking and avoiding smokeless tobacco can significantly reduce the risk of Mouth cancer.
Limit alcohol consumption:
Heavy alcohol use is a major risk factor for Oral cancer. Limiting alcohol consumption can significantly reduce the risk of Oral cancer.
Practice safe sun practices:
Prolonged exposure to the sun can increase the risk of developing lip cancer. Using sunscreen, wearing a wide-brimmed hat, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure can help protect the lips from sun damage.
Eat a healthy diet:
A diet low in fruits and vegetables can increase the risk of Oral cancer. Choosing a diet high in fiber, low in fat, and high in fruits and vegetables can reduce the risk of Mouth cancer.
Practice good oral hygiene:
Regular oral hygiene practices such as brushing, flossing, and rinsing can help prevent Oral cancer.
Undergo regular Mouth cancer screenings:
Regular Mouth cancer screenings, especially if you have any risk factors or if you have any symptoms, can help detect Oral cancer early, when it’s most treatable.
Avoid risky sexual behavior:
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is associated with Oral cancer. To reduce the risk of HPV infection, avoid risky sexual behaviors such as unprotected sex or multiple sexual partners. It’s important to note that these preventive measures are not guaranteed to prevent Mouth cancer, but they can help reduce the risk of developing the disease. It’s always a good idea to have regular Oral cancer screenings and to be aware of any symptoms that persist.
When Should You Visit a Doctor in Nepal?
If you have any of the aforementioned symptoms and are certain you have cancer, you can visit a Head and neck cancer surgeon in Nepal for a checkup. Depending on your preference, you can choose to see a surgical oncologist or a medical oncologist. Your oncologist can advise you on the best course of action. Throughout your treatment plan, you can consider the best cancer surgeon in Nepal, Dr. Prabhat Chandra Thakur, for assistance.

Designation: Consultant & Unit Chief/Program Director Head & Neck Oncology
Qualification: MBBS, MS(ORL-HNS), Fellowship Head & Neck Oncology
Department: Head and Neck Oncology Unit
Special interest: Reconstructive surgery and Minimal Invasive surgery in Head & Neck

2 thoughts on “Mouth Cancer”